Step 1 – Initial Server Setup
I am using an Ubuntu 18.04 t2.medium server with 40GB of attached storage on Amazon AWS. This meets the hardware recommendations for a small/medium size deployment. Although I am deploying this server in AWS, this tutorial should work on any platform running Ubuntu 18.04 (or any Debian-based Linux).
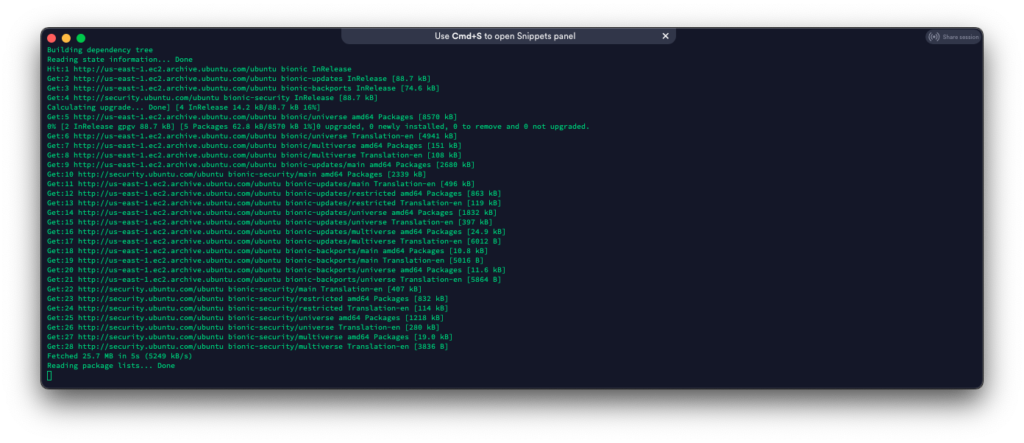
Once the Ubuntu instance is ready, login and start doing some updates:
sudo apt-get update & sudo apt-get upgrade -y
Optional (but highly recommended): Make sure you have a public domain name. This is mandatory if you want to use SSL.
Step 2 – Install git
Since we are pulling Modern Honey Network (MHN) from GitHub, we need to install git.
sudo apt-get install git -y
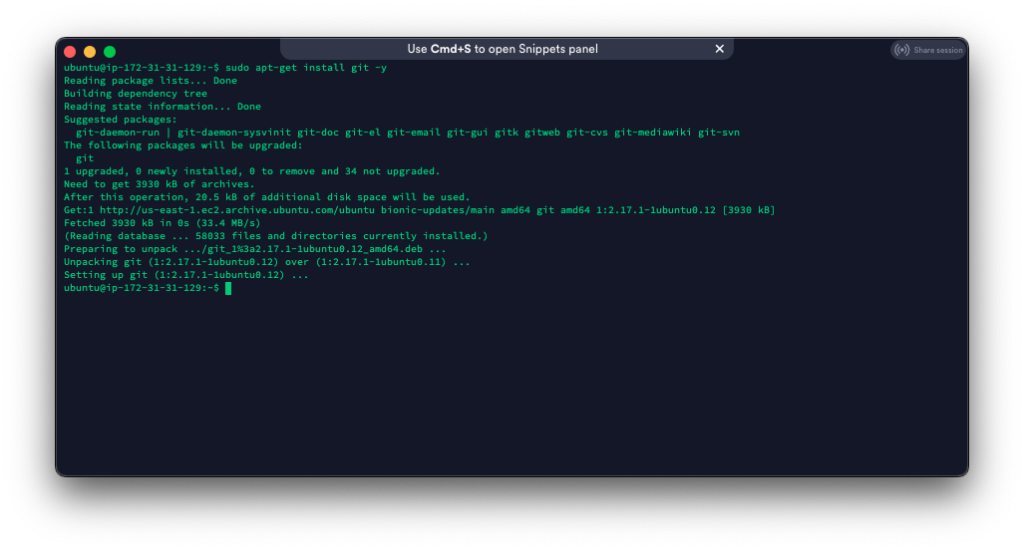
Luckily it looks like git is already installed.
Step 3 – Clone MHN
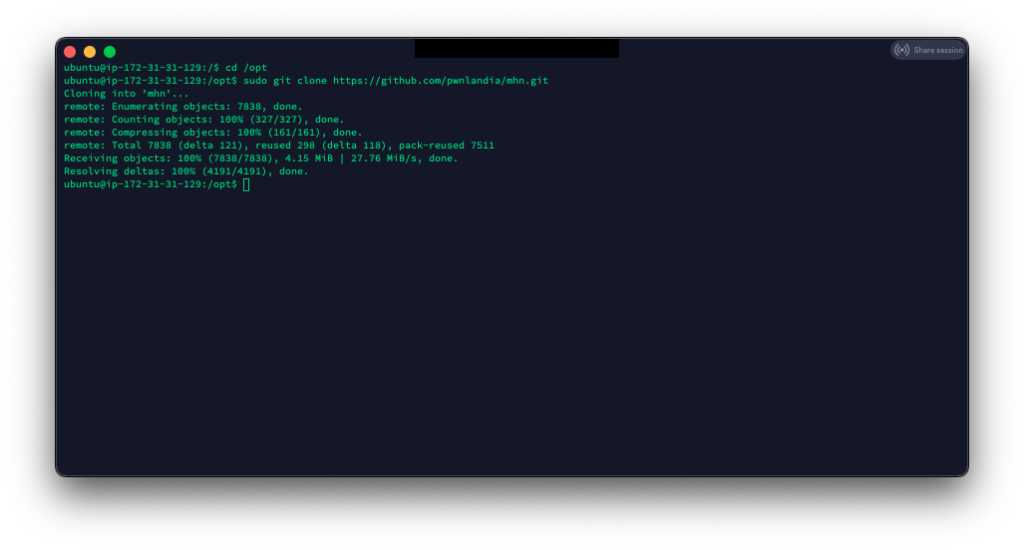
Now, all we have to do is clone MHN into the /opt directory.
cd /opt
git clone https://github.com/pwnlandia/mhn.git
Step 4 – Install MHN
This is where the magic happens! All we have to do is run the setup script, which will install and configure everything for MHN.
cd /opt/mhn/
sudo ./install.sh
Note: This part will take a little bit to complete
At the end of the script it will ask you a few questions:
Do you wish to run in Debug mode?: y/n n
Superuser email: your email address
Superuser password: enter a good complex password
Superuser password: (again): repeat a good complex password
Server base url ["http://IPAddress"]: https://mhn.subproject9.com/ (or use IP)
Honeymap url ["https://domain:3000"]: https://mhn.subproject9.com:3000 (or use IP)
Mail server address ["localhost"]:
Mail Server port [25]:
Use TLS for email?: y/n
Use SSL for email?: y/n
Mail server username ['']:
Mail server password [""]:
Mail default sender [""]:
Path for log file ["/var/log/mhn/mhn.log]:
Note: I am using HTTPS in my settings; this is optional but highly recommended. I am not setting my server up to send emails and leaving the default configuration.
Next, we wait for the database’s initialization and import of SNORT rules. This will take a long time.
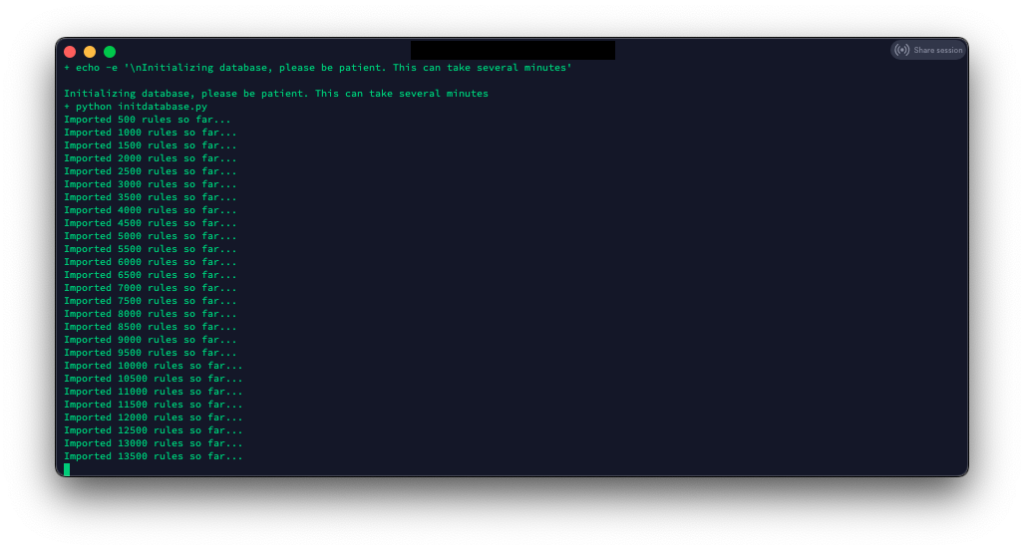
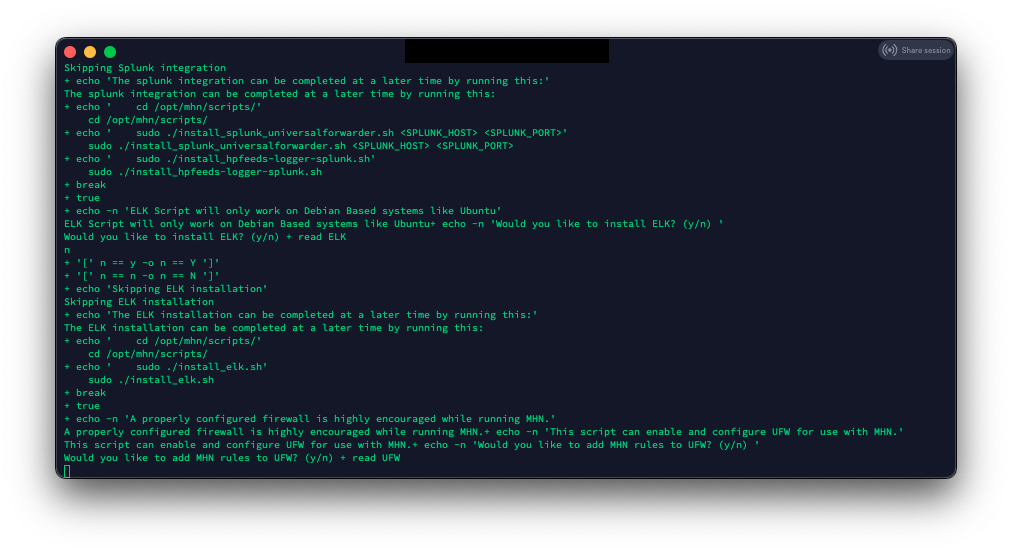
After all the rules load, the install will ask if you want to install Graylog, ELK, and add rules to UFW. In this tutorial, I will not be installing Graylog or ELK. I plan to eventually integrate the alerts/logs into a pre-existing ELK server, but that is for another tutorial.
For this tutorial, I am not allowing the MHN install script to enable and configure the server UFW firewall. If you install MHN for a production environment, ensure you secure your server.
Step 5 – Get SSL Certs using Certbot
First, lets install Certbot:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbot
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install python-certbot-nginx -y
Now we have to edit the default site configuration in NGINX:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/site-available/default
Change the line ‘server_name _;” to your server DNS name ‘server_name mhn.subproject9.com;’
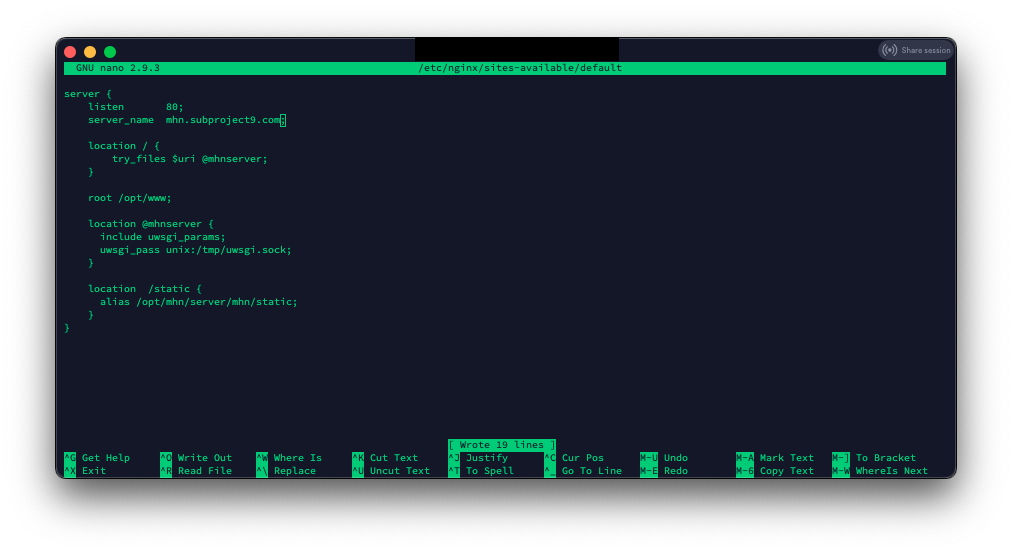
(CTL-O to save, CTL-X to exit)
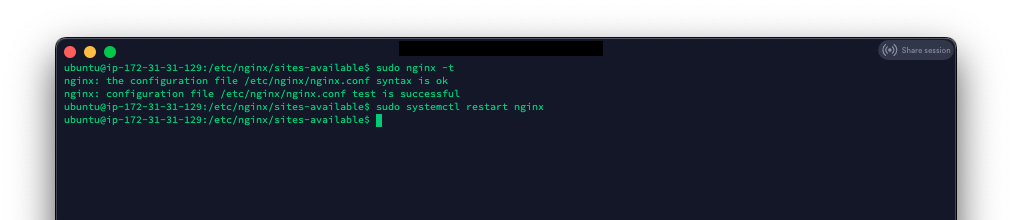
Verify there are no NGINX errors
sudo nginx -t
If there are no errors, restart NGINX
sudo systemctl restart nginx
Now let’s get our SSL cert:
sudo certbot --nginx -d mhn.subproject9.com
If everything goes well, you should see something like this:
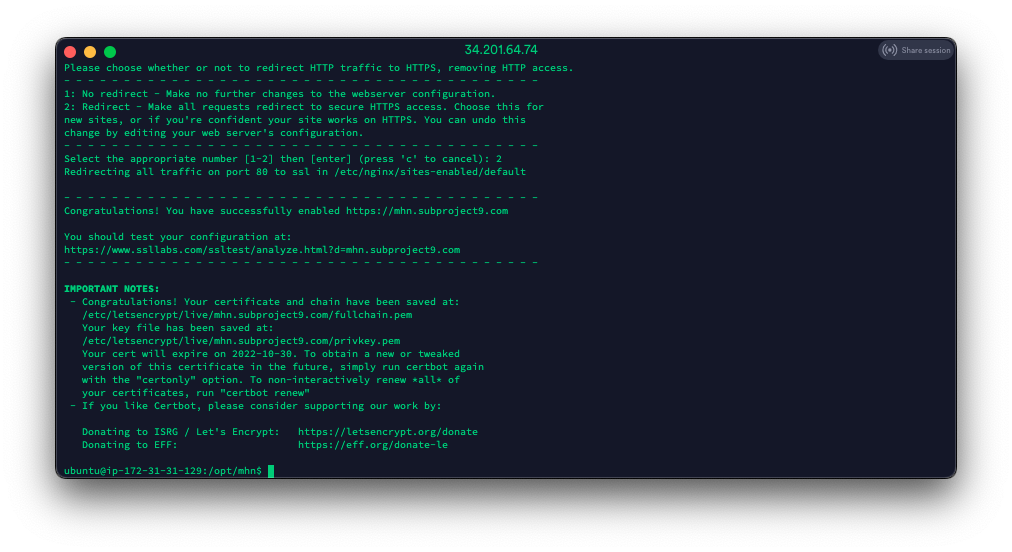
Now, let’s test the interface to make sure everything is working:
Open a browser to your
SUCCESS!
Step 7 – Deploying Honeypots
Deploying honeypots with MHN is extremely easy!
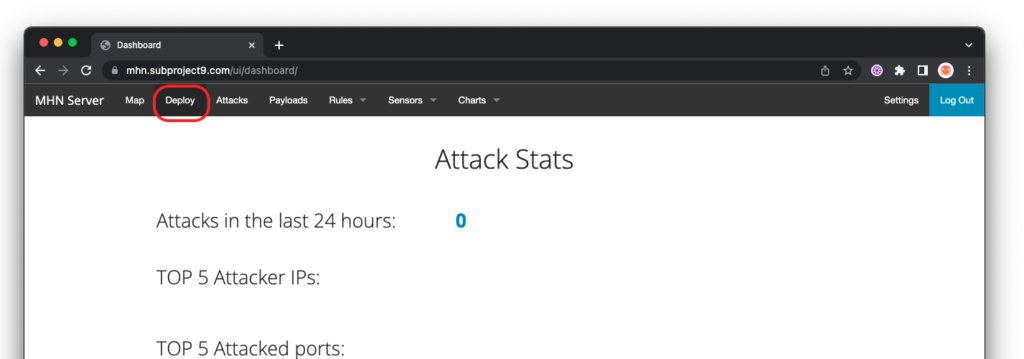
Log into the web interface and select “Deploy” on the top menu:
Select the honeypot you would like to deploy:
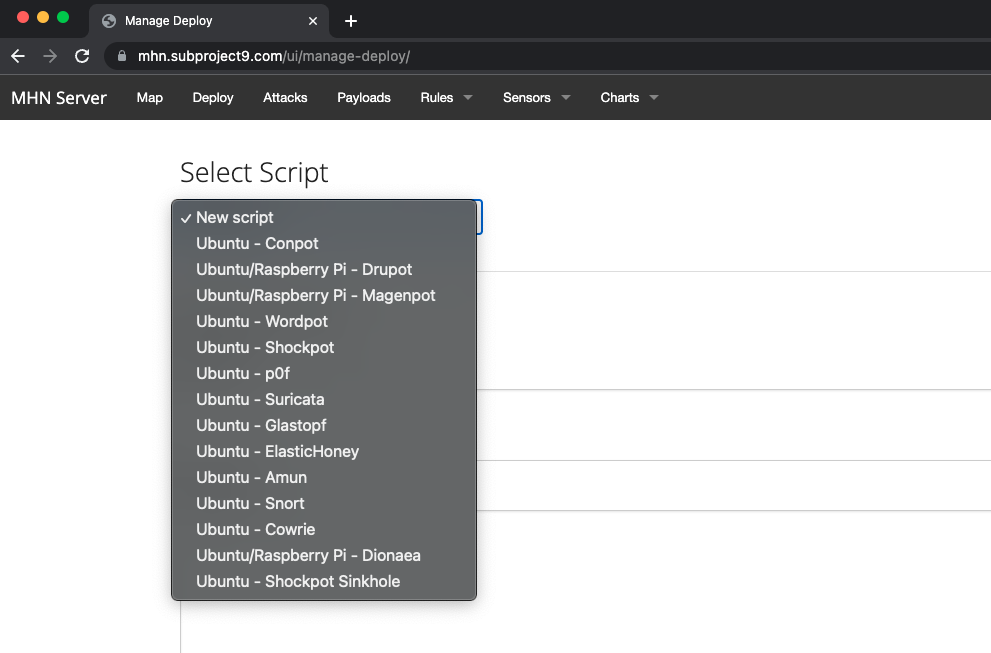
Now, all you have to do is copy the command and drop it a clean install of Ubuntu, Centos 7 or a Raspberry Pi.
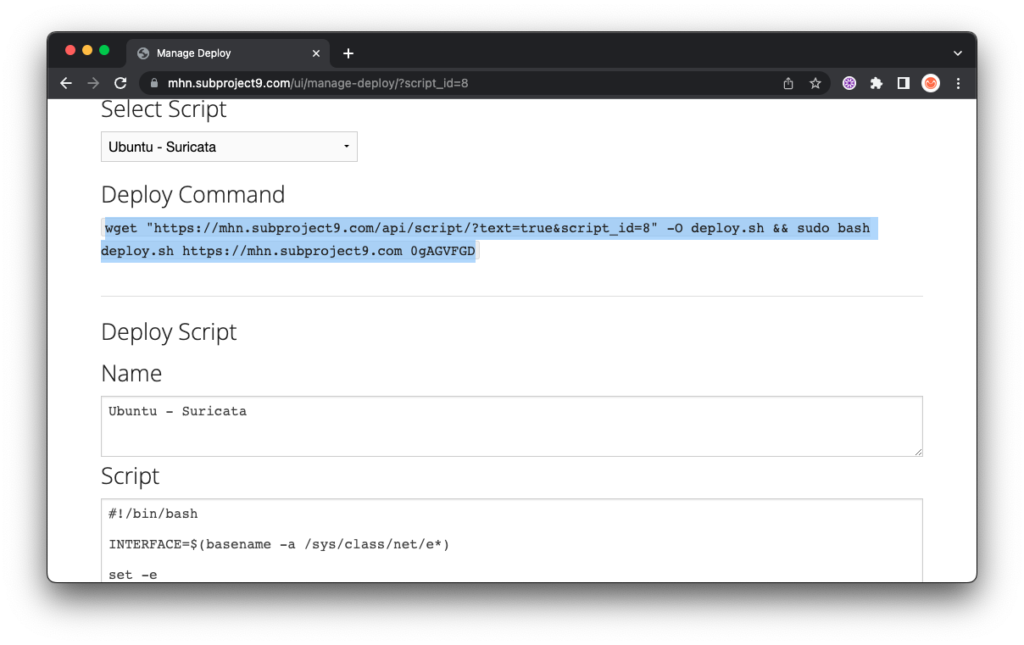
Note: You must install as root and the target server for install must not have any other services deployed.